- B+ tree is a variation of B-tree data structure. In a B+ tree, data pointers are stored only at the
leaf nodes of the tree. In a B+ tree structure of a leaf node differ
from the structure of internal nodes. - The leaf nodes have an entry for every
value of the search field, along with a data pointer to the record (or to the
block that contains this record). - The leaf nodes of the B+ tree
are linked together to provide ordered access on the search field to the
records. - Internal nodes of a B+ tree are
used to guide the search. - Some search field values from the leaf
nodes are repeated in the internal nodes of the B+ tree.
Also Read: What are B-Trees?
Also Read: C Program for AVL Tree Implementation
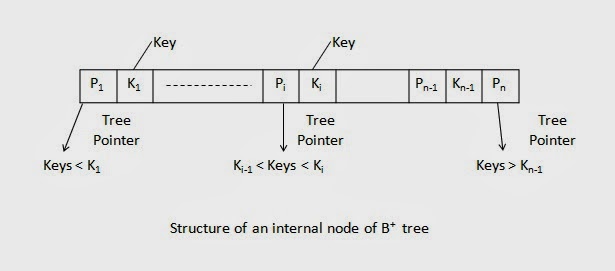
Structure of Internal node
The structure of the internal nodes is
shown below:
shown below:
- Each internal node is of the form < P1,
K1, P2, K2 . . . Pn-1, Kn-1,
Pn > where Ki is the key and Pi is a tree
pointer - Within each internal node, K1 <
K2, . . . < Kn-1 - For all search field value x in the subtree
pointed at by Pi, we have Ki-1 x <= Ki. - Each internal node has at most p tree
pointers. - Each internal node, except the root, has at
least ⌈(P/2)⌉ tree pointers.
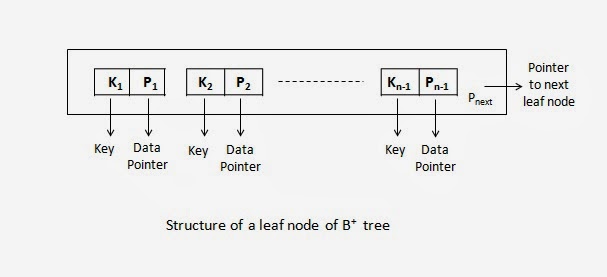
Structure of a leaf node
- Each leaf node is of the form <<K1,
P1>, <K2, P2> . . . <Kn-1,
Pn-1>, Pnext> - Within each leaf node, K1 < K2
. . . < Kn-1. - Pi is a data pointer that points to
the record whose search field value is Ki. - Each leaf node has at least ⌈(P/2)⌉ values.
- All leaf nodes are at the same level.